I’ll admit it my phone and I have a bit of a codependent relationship. I rely on it for everything: directions, work emails, movie tickets, and even to find where I parked my car (which I always forget). So when that dreaded low battery warning flashes, panic sets in faster than a coffee spill on a white shirt. That’s where a power bank battery pack my trusty pocket-sized hero steps in.

That’s where a portable battery pack my trusty pocket-sized hero steps in. Over time, I’ve learned that understanding how a power bank works not only helps me choose better ones but also makes them last longer.
This isn’t another dull tech breakdown. I’ll explain in plain English and yes, we’ll keep it fun and practical.
What You’ll Learn in This Guide
Here’s what this guide covers:
- What a portable charger actually is (beyond the obvious)
- How it stores and transfers power to your devices
- How many full charges can you expect?
- The real pros and cons
- The main types of portable chargers
- Smart tips for choosing one that fits your needs
- How to make it last longer
What Exactly Is a Portable Charger?
If you think of it simply as a backup battery, you’re not wrong. A portable charger, or power bank, is small electronic device that stores electricity so you can refill your gadgets when they run low.

Inside every power bank, three components work quietly together:
- Battery Cells These store energy, usually lithium-ion or lithium-polymer.
- Input/Output Ports Input recharges the power bank; output transfers electricity to your devices.
- Control Circuitry The “brain” that manages voltage, regulates current, and prevents short-circuits or overheating.
That’s it simple but smart engineering.
How Does a Power Bank Work? (Without the Science Headache)
When you plug your power bank into a wall outlet, electricity flows in and is stored inside its cells. Later, when your phone battery drops to 1%, you connect it via cable, and the stored energy flows back out refilling your phone’s battery.
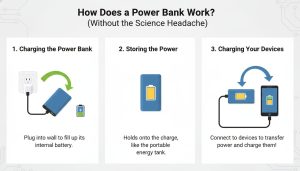
Step by Step Energy Flow
- Energy Intake: You plug in the power bank, and energy begins flowing in.
Its internal circuit regulates the input to prevent overcharging. - Storage: The lithium cells store that energy as chemical potential bottled-up electricity.
- Release: When you connect a phone or tablet, the control chip stabilizes output voltage to suit your device.
- Transfer: Power moves through the cable to your device safely and efficiently.
The chip ensures stable output preventing surges, overheating, or battery damage. It’s a silent guardian working behind the scenes.
Why Knowing This Helps
Before I understood this, I used to leave my power bank plugged in overnight or toss it in my backpack without care. Once I learned how delicate the chemical balance inside is, I started treating it better and my chargers have lasted twice as long.
For a smoother setup, explore our https://pickerzen.com/what-is-a-power-bank-charger/ it walks through charging, indicators, and care basics.
How Many Times Can It Recharge My Phone?
Here’s the quick formula:
Estimated charges = (Power bank capacity × 0.85) ÷ Phone battery capacity
That 0.85 factor accounts for energy loss no transfer is perfectly efficient.
Example:
A 10,000 mAh power bank can recharge a 2,500 mAh phone about three times.
A 20,000 mAh unit? Around six to seven times.
So, if you notice fewer charges than expected, it’s not broken it’s just physics doing its thing.
Pros and Cons of Carrying a Power Bank
Every gadget has its perks and trade-offs. Here’s the honest breakdown:

What’s Great
- Freedom from outlets: Charge anywhere, airports, road trips, or even park benches.
- Different sizes for different needs: From pocket-sized to laptop-grade beasts.
- Multi-device charging: Many can power two or more gadgets simultaneously.
What’s Not So Great
- They also need charging: Your “charger” needs charging. Ironic but true.
- Weight: High-capacity models can be bulky.
- Not all are fast: Cheaper units might lack USB-C PD or Quick Charge support.
- Quality matters: Cheap knockoffs can overheat or fail early.
If you want to compare models safely, check Anker’s detailed list of trusted fast-charging power banks for 2025 (available on their blog)
The Main Types of Portable Chargers

Compact Everyday Power Bank Models
These are the typical ones most people carry small, lightweight, perfect for daily use. They usually range between 5,000–10,000mAh and can fully recharge a phone one to two times.
Solar Powered Power Bank Units
Ideal for campers or frequent travelers. They recharge via sunlight, though I’ll be honest, they’re slow. Solar models are best used as emergency backups rather than main power sources.
Laptop Grade Power Bank Versions
These are built with higher capacity (often above 20,000mAh) and more powerful output. They use USB-C PD (Power Delivery) ports capable of recharging laptops and tablets efficiently.
Wireless Charging Models
The no-cable experience. Just place your phone on top, and it starts transferring energy instantly. They’re perfect for quick top-ups but slightly less efficient than wired connections.
Magnetic (Snap On) Chargers
These latch directly to compatible phones using magnets. Compact, neat, and easy to use while commuting or multitasking.
Personally, I keep one compact charger in my work bag and a heavier one in my travel kit. I learned the hard way that nothing ruins a flight faster than a 1% battery and no outlets nearby.
How to Pick the Right One for You

Choosing a portable charger can feel like choosing a new coffee machine full of specs and confusion. Let’s simplify.
1. Power Bank Capacity Matters
Think about usage.
- Every day: 5,000–10,000 mAh.
- Travel or multiple devices: 20,000 mAh+.
If you want to go deeper into voltage regulation and protection systems, visit https://www.anker.com/blogs/power-banks/a-helpful-guide-to-how-does-a-power-bank-work explains it in simple visuals.
2.Power Bank Charging Speed
Look for USB-C PD or Quick Charge support. These standards can recharge 50% in under an hour.
3. Power Bank Port Types
USB-C is now the universal port. Reversible, faster, and ideal for modern devices. Keep one USB-A port for older gadgets.
4. Build Quality
Durability matters. Choose metal or reinforced plastic casings if you travel often.
5.Brand & Warranty
Well-known brands like Anker, Belkin, and Baseus invest in safety features that cheap knockoffs skip. Trust me I’ve seen too many generic ones fail spectacularly.
How I Make My Power Bank Last Longer
A few small habits can add years to your charger’s lifespan. Here’s what works for me:
- Avoid overcharging Once it’s full, unplug it. Leaving it plugged in constantly wears out the cells.
- Keep it cool High heat shortens battery life. I avoid leaving it in cars or under direct sunlight.
- Recharge occasionally If I don’t use it for weeks, I still top it up to about 50%.
These tiny adjustments have made my chargers last almost double their usual lifespan.
Understanding Battery Health and Lifespan
Every rechargeable battery degrades it’s normal chemistry. Most lithium-based cells last about 500 full cycles before losing capacity.

To slow the process:
- Keep it at moderate temperatures (20–25 °C).
- Avoid constant 100% or 0% charge levels.
- Don’t use it while it’s plugged in that stresses the cells.
If you want to dig into advanced battery care, check Anker’s article on battery health and optimization to learn how professionals extend cycle life.
Think of it like exercise steady use keeps it strong; overdoing it drains it faster.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do I need to drain it before recharging?
No. That’s outdated. Partial charges are fine modern lithium batteries prefer it.
2. Can I carry it on a flight?
Yes, but only in hand luggage. Airlines restrict them in checked bags due to safety rules.
3. How long does it take to recharge?
Small ones (5,000–10,000 mAh) take 3–5 hours. Larger (20,000+) need 8–10 hours unless they support fast charging.
4. Why does it feel warm while charging?
Slight warmth is normal; some energy converts to heat.
If it’s hot to the touch, disconnect and let it cool.
5. Can I charge it with another power bank?
Technically, yes, but it’s inefficient. Use a wall outlet instead.
6. What’s the best model right now?
Depends on use.
For compact daily use, Anker Nano.
For travel Anker PowerCore 20K PD.
Both are safe, efficient, and long-lasting.
Extra Tips for Smart Use
Here are a few lessons I learned (some the hard way):
- Label your cables. It avoids confusion and prevents using the wrong wattage charger.
- Don’t ignore safety certifications. Look for CE, RoHS, or UL markings.
- Keep firmware updated. Some smart chargers let you update software through an app worth doing.
- Avoid using while charging. It creates excess heat and shortens the battery’s lifespan.
- Test once in a while. Every few months, check how much charge it holds versus its original rating.
These small actions make a noticeable difference in long-term performance.
What the Future Holds
The future of portable power looks exciting. Engineers are developing graphene-based batteries that charge in minutes and last longer than lithium-ion batteries. Wireless charging is improving, and smart power banks are emerging ones that auto-adjust voltage, detect device type, and even sync with mobile apps to display real-time stats.
Soon, charging won’t feel like a task; it’ll happen seamlessly like Wi-Fi, quietly in the background.
Final Thoughts
After using countless portable chargers over the years, one thing is clear: it’s not just about convenience anymore. It’s about independence.
Knowing how they work helps me make smarter buying choices and treat them better. A high-quality one isn’t just a gadget it’s insurance for modern life. Whether I’m traveling, stuck in traffic, or lost with a dead phone (again), that small pack of stored power has saved me every time.
So, choose a reliable one, care for it properly, and it’ll return the favor when you need it most. And the next time you watch someone panic at 2% battery, you can just smile because you came prepared.
Pingback: What is a Power Bank Charger? Complete Beginner’s Guide